Molecular Biology Section
Resources
Advanced Molecular Detection
Advanced Molecular Detection
Imagine doing a 10,000-piece jigsaw puzzle in the time it takes to finish a 100-piece puzzle. Apply that to infectious disease control, and that’s AMD at work. Now imagine putting together that 10,000-piece puzzle when key pieces are missing, disease is spreading, and people are dying. AMD gives CDC scientists the “key pieces” they need to protect people from ever-changing infectious disease threats. |
Anthrax
Anthrax
Anthrax is a serious infectious disease caused by gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis. Anthrax can be found naturally in soil and commonly affects domestic and wild animals around the world. Although it is rare, people can get sick with anthrax if they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products. |
Bio-Rad Real-Time PCR Video
Bio-Rad Real-Time PCR Video
Understanding the Real-Time PCR method. |
CaliciNet
CaliciNet
CaliciNet is a national norovirus outbreak surveillance network of federal, state, and local public health laboratories in the United States. CDC launched CaliciNet in 2009 to collect information on norovirus strains associated with gastroenteritis outbreaks in the United States. |
Chikungunya
Chikungunya
Chikungunya virus is transmitted to people by mosquitoes. The most common symptoms of chikungunya virus infection are fever and joint pain. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, or rash. |
Dengue
Dengue
With more than one-third of the world’s population living in areas at risk for infection, dengue virus is a leading cause of illness and death in the tropics and subtropics. As many as 400 million people are infected yearly. |
DNA Tube Pyrosequencing Video
DNA Tube Pyrosequencing Video
The technique was developed by Pål Nyrén and his student Mostafa Ronaghi at the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm in 1996.Procedure "Sequencing by synthesis" involves taking a single strand of the DNA to be sequenced and then synthesizing its complementary strand enzymatically. |
Enteric Diseases
Enteric Diseases
Enteric infections enter the body through the mouth and intestinal tract and are usually spread through contaminated food and water or by contact with vomit or feces. Every year, millions of cases of foodborne illness and thousands of associated deaths occur in the United States. |
How Foodborne Outbreaks are Investigated
How Foodborne Outbreaks are Investigated
When two or more people get the same illness from the same contaminated food or drink, the event is called a foodborne outbreak. Illnesses that are not part of outbreaks are called "sporadic." |
Laboratory Response Network
Laboratory Response Network
A national network of more than 150 labs. |
Norovirus Outbreak Data
Norovirus Outbreak Data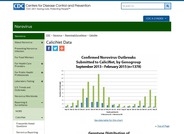
Data about recent outbreaks of Norovirus. |
PulseNet
PulseNet
PulseNet compares the 'DNA fingerprints' of bacteria from patients to find clusters of disease that might represent unrecognized outbreaks. Health officials can't stop an outbreak, and industry and regulatory agencies can't make changes to our food and water delivery systems, if they don't know that outbreaks are occurring. That's where PulseNet comes in. |
PulseNet in the News
PulseNet in the News
News about PulseNet. |
ScienceLearn PFGE Video
ScienceLearn PFGE Video
ESR Scientist Dr Brent Gilpin explains how pulsed field gel electrophoresis is used to separate very large fragments of DNA. DNA from an organism is digested with an enzyme and run on a gel, which gives a barcode that is unique to that organism. This system is used by the PulseNet organisation to identify common sources of disease outbreaks. |

