Keyword Search
Here you can search the content of our website for any combination of keywords. Our custom search engine will perform a search using all of the text you enter, returning results which contain any of the keywords.
You can also fine-tune your searches by using operators. You can indicate that a keyword MUST be present by adding a plus symbol in front of the term. You may also indicate that a keyword must NOT be present by using a minus symbol prefix in front of the term.
EXAMPLE: Immunization +Schedule -Drug -Fee -CHW -Payroll
Please see our Guide to Using Search Engine Operators to learn more about the search engine operators you can use.
52 matches found for “lead”.
-
Lead Poisoning Prevention (topic)
-
Lead in Drinking Water (publication)
[+]
 The Safe Drinking Water Act sets an action level of 15 or less ppb (parts per billion) of lead in drinking water at consumers homes. Drinking water in New Mexico does not naturally contain lead, but lead can get into the water, if lead leaches out of any lead-containing components in the plumbing.
The Safe Drinking Water Act sets an action level of 15 or less ppb (parts per billion) of lead in drinking water at consumers homes. Drinking water in New Mexico does not naturally contain lead, but lead can get into the water, if lead leaches out of any lead-containing components in the plumbing.
-
Tips to Clean Lead Chips and Dust Infographic (publication)
[+]
 Lead dust and chips from lead-based paint are the most common source of lead poisoning. As lead-based paint ages, it can deteriorate (chip, crack, peel) because of weathering.
Lead dust and chips from lead-based paint are the most common source of lead poisoning. As lead-based paint ages, it can deteriorate (chip, crack, peel) because of weathering.
-
Testing for Lead among Children in New Mexico, 2010-2014 (health data)
[+]
 One of the ten great recent public health achievements in the U.S. has been noted to be childhood lead poisoning prevention and control, mostly due to the removal of lead from paint and fuel. While children from all geographic, social and economic levels can be affected, children living in poverty and in older, poorly maintained homes have higher exposure to lead.
One of the ten great recent public health achievements in the U.S. has been noted to be childhood lead poisoning prevention and control, mostly due to the removal of lead from paint and fuel. While children from all geographic, social and economic levels can be affected, children living in poverty and in older, poorly maintained homes have higher exposure to lead.
-
Traditional Pottery May Contain Lead (publication)
[+]
 Lead can affect the nervous system, especially the growing brain, of infants and young children and cause learning and behavior problems that last a lifetime. Lead dust can get into a person’s body by breathing it in, by eating with unwashed hands, or from putting unwashed hands or objects that have lead dust on them into the mouth.
Lead can affect the nervous system, especially the growing brain, of infants and young children and cause learning and behavior problems that last a lifetime. Lead dust can get into a person’s body by breathing it in, by eating with unwashed hands, or from putting unwashed hands or objects that have lead dust on them into the mouth.
-
Child Lead Screening & Case Management Guidelines (publication)
[+]
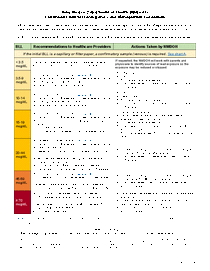 Lead poisoning continues to be an important, preventable environmental health problem. However, only a low number of children in New Mexico are screened for lead each year. This document provides technical guidelines for screening and managing cases of childhood lead poisoning.
Lead poisoning continues to be an important, preventable environmental health problem. However, only a low number of children in New Mexico are screened for lead each year. This document provides technical guidelines for screening and managing cases of childhood lead poisoning.
-
Lead Exposure in Pregnant and Lactating Women (publication)
[+]
 Lead exposure during pregnancy and breastfeeding can result in lasting adverse health effects independent of lead exposure during other life stages. However, to date there has been limited guidance available for clinicians & the public health community regarding the screening and management of pregnant and lactating women exposed to high levels of lead.
Lead exposure during pregnancy and breastfeeding can result in lasting adverse health effects independent of lead exposure during other life stages. However, to date there has been limited guidance available for clinicians & the public health community regarding the screening and management of pregnant and lactating women exposed to high levels of lead.
-
Lead Surveillance Data Users Survey Fact Sheet 2015 (health data)
[+]
 Funding to support the collection, analysis and sharing of surveillance data and other lead-related information with its partners and the public has been used to survey lead data surveillance users. This publication describes the results from our survey and how they will be used to help plan surveillance and communication activities during the next two years.
Funding to support the collection, analysis and sharing of surveillance data and other lead-related information with its partners and the public has been used to survey lead data surveillance users. This publication describes the results from our survey and how they will be used to help plan surveillance and communication activities during the next two years.
-
Protect yourself and your family from lead poisoning (news)
[+]
October 21, 2024 — Exposure to lead can result in serious illness and could require immediate medical attention. Lead exposure in children can cause behavioral and learning problems, hearing loss, and at very high levels, seizures, coma and death. High lead levels can cause high blood pressure, reproductive problems,...
-
Foods that May Reduce Harmful Effects of Lead (publication)
[+]
 Lead is a poison and it interferes with many of the normal functions in the human body. This brochure provides information about nutrition and lead poisoning prevention in young children.
Lead is a poison and it interferes with many of the normal functions in the human body. This brochure provides information about nutrition and lead poisoning prevention in young children.
-
Lead Exposure and Illness in New Mexico Adults Infographic (publication)
[+]
 This infographic is explains about lead exposure and illness in adults and illustrates what the Occupational Health Surveillance Program does including case management services, works with healthcare providers to determine sources of lead, collects data and additional information, and collaborates with OSHA. It also explains how work-related illnesses are tracked.
This infographic is explains about lead exposure and illness in adults and illustrates what the Occupational Health Surveillance Program does including case management services, works with healthcare providers to determine sources of lead, collects data and additional information, and collaborates with OSHA. It also explains how work-related illnesses are tracked.
-
Adult Lead Exposure Management Guidelines (publication)
[+]
 Lead exposure can have adverse effects on various organs and systems in the body, resulting in negative health effects, both acute and chronic, depending on the level of exposure or dose, exposure duration, and other factors including dietary. In New Mexico, industries where lead exposure is common include public safety, radiator repair, mining and construction.
Lead exposure can have adverse effects on various organs and systems in the body, resulting in negative health effects, both acute and chronic, depending on the level of exposure or dose, exposure duration, and other factors including dietary. In New Mexico, industries where lead exposure is common include public safety, radiator repair, mining and construction.
-
Lead in Firing Ranges (publication)
[+]
 This is a personal protective equipment check list for workers explains a few simple steps you can take to reduce your exposure to lead at indoor firing ranges. These steps include wearing a respirator, coveralls including shoe covers, safety goggles, and chemical resistant gloves. It also provides some additional website resource links so you can learn more about preventing occupational exposures to lead and noise at indoor firing ranges.
This is a personal protective equipment check list for workers explains a few simple steps you can take to reduce your exposure to lead at indoor firing ranges. These steps include wearing a respirator, coveralls including shoe covers, safety goggles, and chemical resistant gloves. It also provides some additional website resource links so you can learn more about preventing occupational exposures to lead and noise at indoor firing ranges.
-
Lead Exposure in Children: Prevention, Detection, and Management (resource)
[+]
 Fatal lead encephalopathy has disappeared and blood lead concentrations have decreased in US children, but approximately 25% still live in housing with deteriorated lead-based paint and are at risk of lead exposure with resulting cognitive impairment and other sequelae.
Fatal lead encephalopathy has disappeared and blood lead concentrations have decreased in US children, but approximately 25% still live in housing with deteriorated lead-based paint and are at risk of lead exposure with resulting cognitive impairment and other sequelae.
-
Lead Tips for Pregnant Women (resource)
[+]
 Lead poisoning is caused by breathing or swallowing lead. Lead can pass from a mother to her unborn baby.
Lead poisoning is caused by breathing or swallowing lead. Lead can pass from a mother to her unborn baby.
-
Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention (resource)
[+]
 Childhood lead poisoning is preventable. Before some uses of lead were restricted, approximately 88% of preschool children in the United States had lead levels high enough to cause serious health effects.
Childhood lead poisoning is preventable. Before some uses of lead were restricted, approximately 88% of preschool children in the United States had lead levels high enough to cause serious health effects.
-
Lead Abatement vs Lead RRP (resource)
[+]
 Abatement is a specialized activity designed to address lead in the home. RRP activities (including most home contracting work) disturb paint as a consequence of the activity, but they are often undertaken for reasons unrelated to lead issues.
Abatement is a specialized activity designed to address lead in the home. RRP activities (including most home contracting work) disturb paint as a consequence of the activity, but they are often undertaken for reasons unrelated to lead issues.
-
Adult Blood Lead Epidemiology & Surveillance (resource)
[+]
 Objective is to build state capacity to initiate, expand, or improve adult blood lead surveillance programs which can accurately measure trends in adult blood lead levels and which can effectively intervene to prevent lead over-exposures.
Objective is to build state capacity to initiate, expand, or improve adult blood lead surveillance programs which can accurately measure trends in adult blood lead levels and which can effectively intervene to prevent lead over-exposures.
-
Lead Surveillance Data Users Survey Report 2015 (health data)
[+]
 The purpose of this report is to characterize the use of and need for different types of lead-related data among New Mexico’s communities and decision-makers, as well as housing, child development, and health professionals.
The purpose of this report is to characterize the use of and need for different types of lead-related data among New Mexico’s communities and decision-makers, as well as housing, child development, and health professionals.
-
Don’t Take Lead Home From Your Job (publication)
[+]
 This document answers many questions about workers who are at risk of bringing home lead from work.
This document answers many questions about workers who are at risk of bringing home lead from work.
-
Toxic Levels of Lead in Treats (publication)
[+]
 California and U.S. health officials have detected dangerous levels of lead in 112 distinct brands of candy – most of them made in Mexico. One in four candy and wrapper samples have come up high since 1993, records show. But much of this information about tainted candy has been kept from parents and public health workers.
California and U.S. health officials have detected dangerous levels of lead in 112 distinct brands of candy – most of them made in Mexico. One in four candy and wrapper samples have come up high since 1993, records show. But much of this information about tainted candy has been kept from parents and public health workers.
-
What Parents Should Know About Childhood Lead Poisoning (publication)
[+]
 This document contains a list of frequently asked questions for parents to learn more about childhood lead poisoning.
This document contains a list of frequently asked questions for parents to learn more about childhood lead poisoning.
-
Lead Dust in Imported Vinyl Mini-Blinds Infographic (publication)
[+]
 This infographic explains how some imported plastic/vinyl mini-blinds can be lead hazards and provides a checklist to help you determine if you may have a hazard in your home.
This infographic explains how some imported plastic/vinyl mini-blinds can be lead hazards and provides a checklist to help you determine if you may have a hazard in your home.
-
Lead in Tap Water (publication)
[+]
 Tips to reduce your exposure to lead in tap water.
Tips to reduce your exposure to lead in tap water.
-
Lead in Drinking Water (publication)
[+]
 General information about lead in drinking water.
General information about lead in drinking water.
-
CDC Advisory - High Blood Lead Levels in Children Consuming Recalled Cinnamon (publication)
[+]
 CDC Advisory - High Blood Lead Levels in Children Consuming Recalled Cinnamon
CDC Advisory - High Blood Lead Levels in Children Consuming Recalled Cinnamon
-
Prevent Lead Poisoning Start Now CDC (publication)
[+]
 Prevent Lead Poisoning Start Now CDC
Prevent Lead Poisoning Start Now CDC
-
Lead and Pregnancy Infographic (Spanish) (publication)
[+]
 Lead and Pregnancy Infographic Spanish
Lead and Pregnancy Infographic Spanish
-
Child Lead Exposure Questionnaire (publication)
[+]
 Use this questionnaire to help you and your health care provider to decide if your child needs a blood test for lead.
Use this questionnaire to help you and your health care provider to decide if your child needs a blood test for lead.
-
Prevention of Childhood Lead Toxicity (publication)
[+]
 Prevention of Childhood Lead Toxicity
Prevention of Childhood Lead Toxicity
-
Prenatal Lead Risk Questionnaire (publication)
[+]
 This questionnaire provides a list of questions intended to gather all the essential information required to help those who are pregnant or planning pregnancy determine if they need a blood test for lead.
This questionnaire provides a list of questions intended to gather all the essential information required to help those who are pregnant or planning pregnancy determine if they need a blood test for lead.
-
Instructions for Lead and Copper Sample Collection (publication)
[+]
 These instructions explain how to collect lead and copper samples.
These instructions explain how to collect lead and copper samples.
-
Some Imported Products Contain Lead (publication)
[+]
 Some Imported Products Contain Lead
Some Imported Products Contain Lead
-
Lead and Pregnancy Infographic (English) (publication)
[+]
 Lead and Pregnancy Infographic
Lead and Pregnancy Infographic
-
Lead Renovation Repair and Painting Rule (resource)
[+]
 Requires the use of lead-safe work practices to ensure that common renovation activities like sanding, cutting and demolition, which can create hazardous lead dust, are conducted properly by trained and certified contractors or individuals.
Requires the use of lead-safe work practices to ensure that common renovation activities like sanding, cutting and demolition, which can create hazardous lead dust, are conducted properly by trained and certified contractors or individuals.
-
REMINDER: Centers for Disease Control warns consumers about high blood lead levels in children potentially connected to cinnamon applesauce products (news)
[+]
November 21, 2023 — As reported by media across the country, on November 13, the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) issued a Health Alert that it is investigating a possible link between three brands of recalled cinnamon applesauce products and high blood lead levels in children. Multiple states have reported potential...
-
Department of Health Urges Moderation this Halloween (news)
[+]
October 26, 2016 — Halloween is a great opportunity for parents to talk to their children about eating healthy and promoting good oral hygiene that will lead to healthy teeth. The message isn’t that candy is bad, but that candy and other sweets in excess can lead to cavities.
-
FDA Issues Notice of Possible Lead Poisoning Risk in Children (news)
[+]
April 13, 2015 — The New Mexico Department of Health received an alert from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regarding a powdered product called “Bo Ying compound,” which may contain high levels of lead.
-
Occupational Lead Poisoning Course (resource)
[+]
 This CME course will focus on the overview of adult/occupational lead poisoning in California.
This CME course will focus on the overview of adult/occupational lead poisoning in California.
-
Lead Safety in the Workplace (resource)
[+]
 Many worry about lead in their homes or in the environment, but for some, the workplace may offer the greatest potential for exposure.
Many worry about lead in their homes or in the environment, but for some, the workplace may offer the greatest potential for exposure.
-
Childhood Lead Poisoning (resource)
[+]
 The information on this page of the New Mexico Environmental Public Health Tracking Network focuses on lead poisoning (exposure, risk, and protection). Included is an interactive data query producing data based on population and geography.
The information on this page of the New Mexico Environmental Public Health Tracking Network focuses on lead poisoning (exposure, risk, and protection). Included is an interactive data query producing data based on population and geography.
-
Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Course (resource)
[+]
 This CME course focuses to raise awareness of recent changes in Centers for Disease Control guidelines for evaluating elevated blood lead levels in children between 6 months and 6 years of age.
This CME course focuses to raise awareness of recent changes in Centers for Disease Control guidelines for evaluating elevated blood lead levels in children between 6 months and 6 years of age.
-
Falls Among Older Adults in New Mexico (health data)
[+]
 An estimated one in three adults ages 65 years and older experience a fall each year. Falls can cause fractures, head trauma and other injuries that lead to hospitalization, disability and premature death. Hip fractures and traumatic brain injuries are the most serious fall-related injuries in older adults. Over 90% of hip fractures among older adults are caused by falls, and in 2005, fall-related TBI accounted for 50% of unintentional fatal falls among older adults.
An estimated one in three adults ages 65 years and older experience a fall each year. Falls can cause fractures, head trauma and other injuries that lead to hospitalization, disability and premature death. Hip fractures and traumatic brain injuries are the most serious fall-related injuries in older adults. Over 90% of hip fractures among older adults are caused by falls, and in 2005, fall-related TBI accounted for 50% of unintentional fatal falls among older adults.
-
Alcohol Poisoning Death in New Mexico, 1999-2003 (health data)
[+]
 Alcohol poisoning results from the rapid ingestion of large quantities of alcohol, which can lead to very high blood alcohol concentrations and death. In the past several years, the highly publicized alcohol-poisoning deaths of college students in a number of states have focused much-needed national and state attention on the risks of binge drinking in the underage and college-age population.
Alcohol poisoning results from the rapid ingestion of large quantities of alcohol, which can lead to very high blood alcohol concentrations and death. In the past several years, the highly publicized alcohol-poisoning deaths of college students in a number of states have focused much-needed national and state attention on the risks of binge drinking in the underage and college-age population.
-
Substance Use During Pregnancy in New Mexico, (health data)
[+]
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecol-ogists (ACOG) recommends avoiding the use of psy-choactive substances during pregnancy.1 However, an article by Branum and Ahrens2 reports that, on average, women are unaware of being pregnant until five to six weeks into their pregnancy. This is a critical public health concern because substance use during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage, congenital anomalies, fetal al-cohol spectrum disorders (FASDs), and neonatal absti-nence syndrome (NAS), among others
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecol-ogists (ACOG) recommends avoiding the use of psy-choactive substances during pregnancy.1 However, an article by Branum and Ahrens2 reports that, on average, women are unaware of being pregnant until five to six weeks into their pregnancy. This is a critical public health concern because substance use during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage, congenital anomalies, fetal al-cohol spectrum disorders (FASDs), and neonatal absti-nence syndrome (NAS), among others
-
April is Alcohol Awareness Month (news)
[+]
April 22, 2024 — April is national Alcohol Awareness Month, a time to raise awareness and understanding of alcohol abuse. Over time, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to the development of chronic diseases and other serious issues that affect your quality of life, both physically and mentally.
-
Salmonella Associated with Baby Birds (news)
[+]
March 13, 2018 — The New Mexico Department of Health cautions residents about the potential for annual spring time purchases of baby chicks to lead to Salmonella infections. Families are advised to keep baby chicks or other baby birds out of their homes and use caution in order to avoid the infection.
-
Summer travel brings risk of measles (news)
[+]
May 2, 2025 — Community events can lead to measles exposure.
-
Be careful with alcohol use this summer (news)
[+]
July 2, 2025 — As temperatures and summer activities increase, so does the likelihood of binge drinking and the risk of alcohol-related accidents and injuries, which sometimes lead to death.
-
You can protect yourself from smoke hazards during wildfires (news)
[+]
May 20, 2024 — May is Wildfire Awareness Month and the New Mexico Department of Health (NMHealth) is urging New Mexicans to be prepared in the event of wildfires. Climate change has impacted New Mexico, with increased and persistent heat as well as strong winds. Both these conditions lead to an increased risk of w...
-
Dr. Laura Parajon Joins Department of Health as Deputy Secretary (news)
[+]
February 3, 2021 — Experienced clinician, community health worker, will help lead COVID-19 vaccination effort
-
Reporting & Surveillance @ 1-833-796-8773 (hotline)
[+]
Available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year to address public health concerns that need to be addressed immediately such as: plague, measles, hantavirus, meningococcal disease, and pertussis. The number can also be called to ask questions about potential outbreaks such as influenza in a healthcare facility, suspected foodborne disease linked to food establishments, environmentally-related conditions such as lead, carbon monoxide, or mercury poisoning, and reporting and receiving recommendations about animal bites.









































